To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.

Decimal Digit: Definition, Properties, Applications, & Examples

Publish Date: 06 Nov, 2023
Table of Content
Decimal digits play a fundamental role in our everyday lives, shaping the way we handle numbers and perform calculations. This article will explore the decimal digit, including its definition, features, and applications. Understanding decimal digits is crucial whether you are a student, professional, or simply interested in numbers. So, let's embark on this journey to unravel the secrets of decimal digits!
What is Decimal Digit?
A decimal digit is the symbol used in the decimal system to represent figures. The decimal system, frequently known as the base-10 system, is a ten-number numeric system conforming to the figures 0 through 9. These integers may be combined to represent any positive or negative integer.
Decimal Number System:
The base of a decimal number is the generality of place value which states that the value of a number is determined by the position of each number. The system of decimal digits is greatly used in the world.
The first digit is for ones, the second for tens, the third for hundreds, etc. Using this positional value system, we may express digits of varying magnitudes with a limited number of digits.
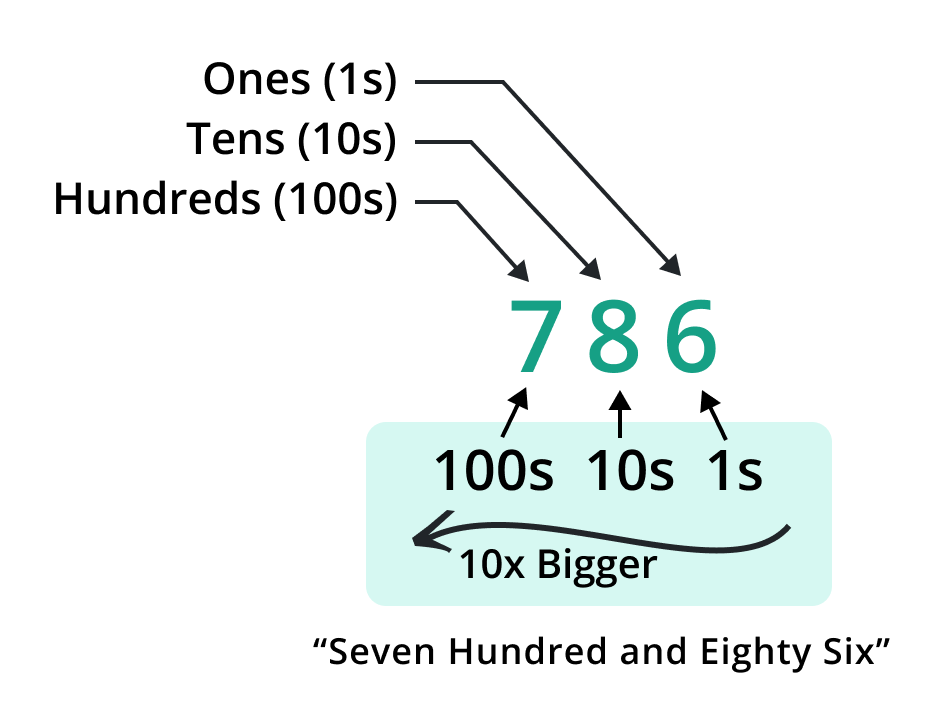
Properties of Decimal Digits:
The properties of decimal digits are as follows:
- Positional Value
- Place Value
- Significance
Positional Value:
The positional value of decimal digits is crucial for understanding and working with numbers. Each digit holds a specific place value based on its position within a number.
For instance,
In the number 357.89, digit 3 has a value of 300 because it is in the hundreds place, while digit 8 represents 0.08 as it is in the hundredth place.
Place Value:
Place value suggests the value of a digit in relation to its position inside a number. In a decimal-digit system, the value of each number increases by a factor of ten as we move from right to left. This means that the number placed ten is ten times bigger than the number in position one.
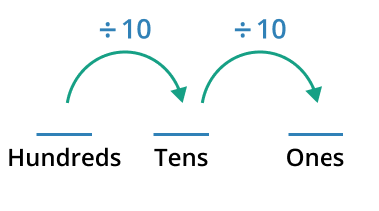
Significance:
Decimal digits are important because they allow us to correctly express fractions and rational sums. Unlike other number systems such as binary or hexadecimal, decimal digits give a clear and visual representation of daily values.
Decimal Digits in Arithmetic Operations
Decimal digits are extensively used in arithmetic operations which are as follows:
- Addition and Subtraction
- Multiplication and Division
Addition and Subtraction:
When adding or subtracting numbers with decimal digits, we align the digits based on, their place values and perform the operation column by column. The result is a sum or difference that maintains the decimal positions of the original numbers.
For example,
When adding 3.14 and 2.76, we add the digits in the one’s place (4 + 6 = 10), carry the 1 to the next column, and then add the digits in the tenth place (1 + 1 + 3 = 5). The result is 5.90.
Multiplication and Division:
In multiplication and division, decimal digits are handled similarly to whole numbers. After performing the operation, we need to adjust the decimal position in the result. The decimal places in the source numbers determine the number of decimal places in the outcome.
E.g.,
when multiplying 2.5 by 0.3, we ignore the decimal places in the beginning (25 multiplied by 3 equals 75) and then count the decimal places in the original numbers (1 + 1 = 2). Then the result, which we get, is 0.75.
Applications of Decimal digits:
Decimal digits find extensive use in various real-life applications due to their precision and versatility. Here are a few areas where decimal digits are commonly applied:
Finance and Accounting:
In finance and accounting, decimal digits are crucial for accurate calculations of money, investments, and financial statements. Whether it's calculating interest, determining profits and losses, or managing budgets, the decimal system ensures precision in financial calculations.
Measurement and Conversions:
Decimal digits play a vital role in measurement systems. They allow us to represent fractional quantities and make precise measurements. Whether it's measuring length, weight, volume, or time, decimal digits enable us to quantify and convert units with ease.
Scientific Notation:
Scientific notation, often used in scientific and mathematical fields, relies on decimal digits. It provides a compact and convenient way to express extremely large or small numbers. By utilizing powers of 10 and decimal digits, scientific notation simplifies calculations and the representation of significant figures.
Statistics and Data Analysis:
Decimal digits are fundamental in statistics and data analysis. They enable us to represent and analyze data accurately. Whether it's calculating means, medians, or standard deviations, decimal digits ensure precise measurements and meaningful interpretations.
Example section of Decimal-digit
Some examples of decimal digits with different mathematical operations are as follows:
Example 1:
Add the following decimal digit.
314, 144.
Solution:
Step 1: Align the digits in a horizontal way.
3 1 4
+ 1 4 4
Step 2: Apply the arithmetic operation of addition.
3 1 4
+ 1 4 4
4 5 8
So, the given answer is 458.
Example 2:
Multiply the given decimal digits.
321, 12.
Solution:
Step 1: Align the digits in horizontal form.
3 2 1
× 1 2
Step 2: Apply the arithmetic operation of Multiplication.
3 2 1
× 1 2
6 4 2
+ 3 2 1 ×
3 8 5 2
So, the answer to the given decimal digit is 3852.
Conclusion
Decimal digits are the building blocks of the decimal number system, empowering us to work with numbers in a precise and comprehensive manner. From basic arithmetic operations to complex financial calculations and scientific endeavors, decimal digits are at the core of numerous applications.
We may gain a better understanding of their importance in our everyday lives by learning about their qualities, utility, and real-world applications. After reading this material thoroughly, everyone should be able to grasp the fundamental notion of decimal digits.
