To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.

Identity Property of One: Definition, Proof, Applications, & Examples
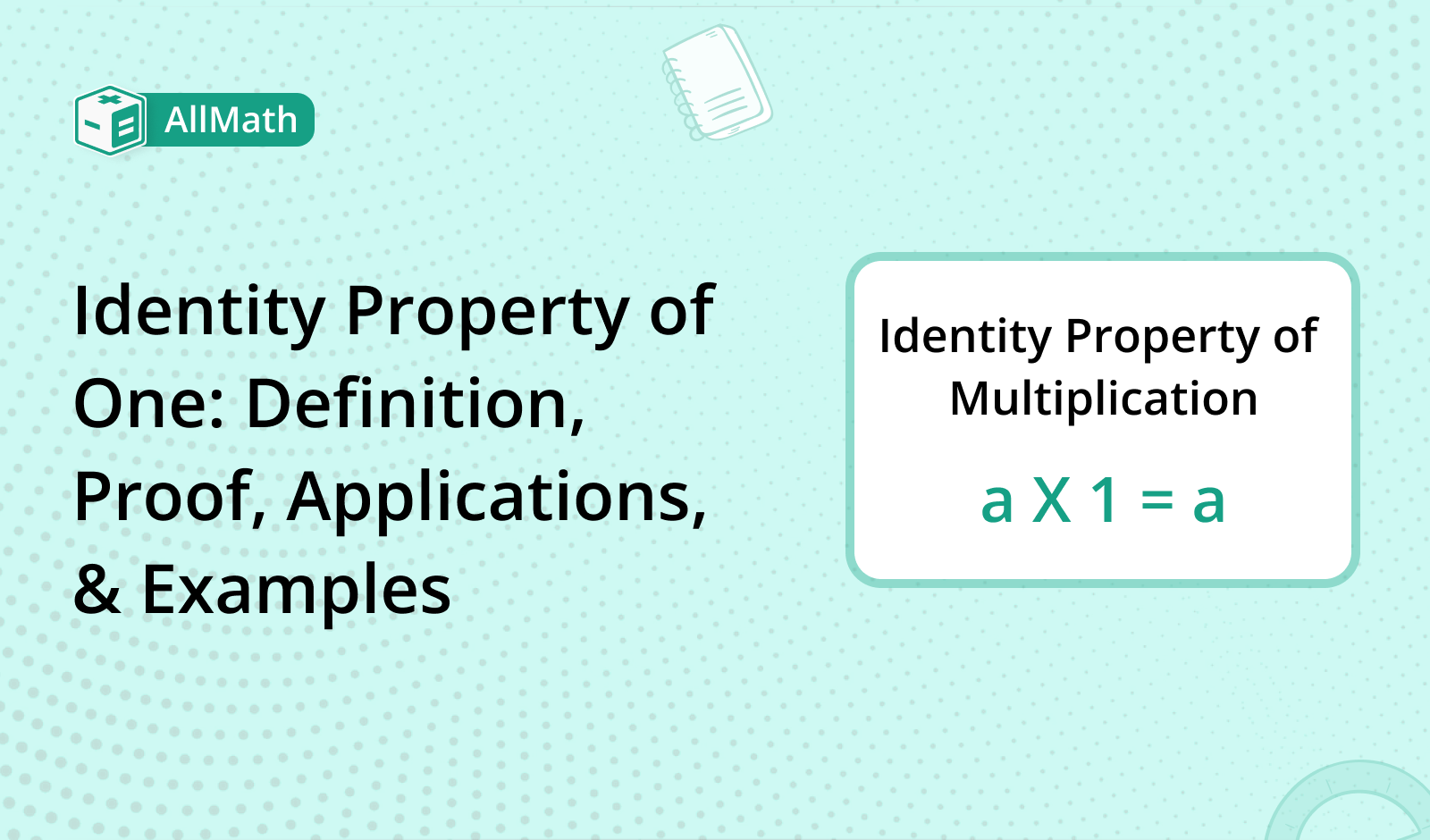
Table of Content
The identity property of one is a crucial concept in mathematics that simplifies calculation and reduces errors. It provides a starting point for more complex algebraic concepts. It says that the result of multiplying any integer by one is that number. The concept of identity property of one is used in algebra, number systems, set theory, and Boolean algebra.
In this article, we will discuss the definition of identity property of one, and its properties. In the example section, we will solve the different examples of the identity property of one (1).
Definition and Exploitation
The identity property of one is also known as multiplicative identity property. It states that the result does not change when 1 is multiplied by any number. In other words, one acts as the identity element for multiplication.
The Identity property of one can be defined as follows: For any real number 'a', the product of 'a' and 1 is equal to 'a.'
In mathematical notation, it can be represented as:
a × 1 = a
or
1 × a = a
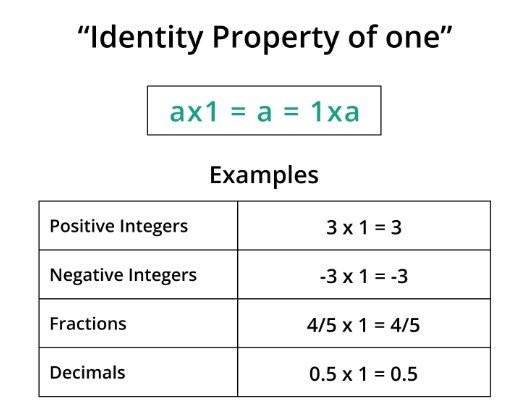
This property holds for all real numbers, whether they are positive, negative, or zero.
Proof of Identity Property of One
Proof 1: Identity property of one
To prove the identity property of one, we will consider an arbitrary real number ‘a’ and multiply it by 1. This gives us.
a × 1 = a
We can divide both sides by ‘a’
a × 1/a = a/a
This simplifies to:
1 = 1
Therefore the equation is true for any a, we have proven the identity property of one.
Proof 2: Unique Identity Property
To prove that one is the unique element with the identity property for multiplication. Suppose there is another number b such that b × a = a, for all numbers a. Then,
b × 1 = 1
We also know that 1 × 1 = 1. Therefore, we have two equations:
b × 1 = 1
1 × 1 = 1
Since these equations are equal, their corresponding coefficient must also be equal. That means b = 1.
Therefore, the only number with the identity property for multiplication is 1.
Applications of Identity Property of One in Mathematics
The identity property of one is used in various branches of mathematics to simplify calculations, derive mathematical theorems, and establish foundational principles. Here are some common applications of identity property:
Arithmetic and Algebra
In arithmetic and algebra, the identity property of one is used extensively. It allows for the simplification of calculations and the manipulation of algebraic expressions. By multiplying terms or variables by one, the value of the expression remains unchanged, facilitating the solving of equations and establishing relationships between different algebraic expressions.
Number Systems
The identity property of one applies to various number systems, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and real numbers. Regardless of the number system, multiplying any number by one results in the original number. This property reinforces the concept that one acts as the multiplicative identity in all these number systems.
Boolean Algebra and Logic
In the realm of Boolean algebra and logic, which deals with binary variables and truth values, the identity property of one is significant. Multiplying a Boolean variable by one always gives the same value as the input. This property is used in designing and analyzing digital circuits.
Mathematical Proofs and Theorems
The identity property of one is frequently used in mathematical proofs and theorems. Mathematicians can derive and prove various mathematical properties and principles by using one as the identity element for multiplication. This property provides a foundational understanding of multiplication and its behavior.
Examples of Identity Properties of One in real life
The Identity Property of one plays a significant role not only in theoretical calculations but also in real-life scenarios. Let’s explore examples of the Identity Property of One in real life.
- If you have a pack of 20 identical candies and you distribute them to 20 children, each child will receive one candy. The product of the number of candies by one gives the same amount of candies.
- Imagine you have a recipe that requires two cups of flour. If you need to increase a recipe's yield, multiply all ingredients by a certain factor. Multiplying two cups of flour by one results in the same amount.
- When calculating the total cost of items, multiplying the price of each item by one represents the unchanged value of that item. If a t-shirt costs 1o dollars, multiplying $10 by one gives you the original price.
Solved Examples of Identity Properties of One in Mathematics
Example 1:
If 15 × a = 15, Determine the value of a. Identify the property being used.
Solution:
Given:
15 × a = 15
a = 15 / 15 = 1
a = 1
Therefore, 15 × 1 = 15
Here, the property used is the Identity property of 1.
Example 2:
Which of the two-equation shows the identity property of one?
- 37 × 1 = 37
- - 37 × - 1 = 37
Solution:
- The equation 37 × 1 = 37 expresses the identity property of 1 because when the number 37 is multiplied by one, the result is the same as the original number itself, which is 37.
- The equation -37 × -1 = 37 does not show the identity property of one because when -37 is multiplied by -1, the result is 37, which is different from the original number -37.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the Identity Property of One, its definition, and its application. We described all proof related to it. We provided real-world examples of it to understand its importance. We did solve mathematical examples of the identity property of one for you.
