To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.

Impossible Event: Definition, Types, & Examples

Publish Date: 08 Aug, 2023
Table of Content
Let's look at the concept of an event before delving into the impossible event. A subset of all of the possible experimental results is an event. In simpler terms, an event represents a particular occurrence that we are interested in while experimenting.
If the experiment is a die toss, the sample space is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; which is the set of all possible outcomes of the experiment. {1, 2}, {1} are events of the given sample space.
An impossible event has zero probability of happening. The basic concepts of an impossible event will be discussed in this article along with examples.
What are Impossible Events?
An impossible event is an event that is not possible to take place. This means there is no chance of the event occurring; no matter how many times you try. Rolling a 9 on a standard die is impossible because there are only 6 possible outcomes, and not of them are 9. Hence, its probability will be 0.
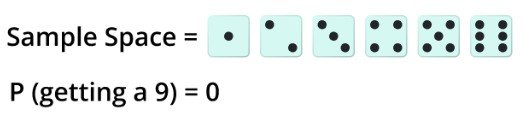
Some other examples of impossible events:
- Getting a seven on a regular die.
- Select a pink ball from a basket that contains only blue balls
- Receiving both heads and tails while flipping a coin.
It is important to be able to identify impossible events because they can significantly affect the probability of other events. When calculating the probability of rolling an odd number on a die, the event of rolling 7 can be ignored because it is impossible.
Types of Impossible Events
There are different types of impossible events with unique characteristics. Here are some of the most common types of impossible events:
Violations of Fundamental Laws
These events contradict well-established scientific principles and fundamental laws of nature. An event that violates the law of conservation of energy or the law of gravity would be considered impossible.
Logical Contradictions
These events involve logical inconsistencies or contradictions. Examples include events like a square circle, which are logically impossible and cannot exist.
Mathematical Impossibilities
These events go against mathematical principles or axioms. For instance, dividing a number by zero or finding a real number that is both positive and negative are mathematical impossibilities.
Physical Impossibilities
These events oppose our universe's physical constraints and limitations. Examples include traveling faster than the speed of light or creating perpetual motion machines that violate the laws of thermodynamics.
The Probability of Impossible Events
When we talk about probabilities, we usually assign numbers between 0 and 1. Zero means impossible, and 1 means certain. Since an impossible event cannot happen, its probability is always zero.
The total number of potential outcomes to determine probability is divided by the number of favorable outcomes. However, an impossible event has no favorable outcomes because it can never occur. Hence, the impossible event will have zero probability.
Implications of Impossible Events in Real-Life Scenarios
A few implications of impossible events in real-life scenarios are:
Scientific research
Recognizing impossible events is important because it helps us understand the boundaries of our experiments and the limitations of what can happen. It allows researchers to focus on realistic outcomes and ensures that their findings are reliable and reproducible.
Decision-making
Impossible events help us eliminate unrealistic options and concentrate on feasible alternatives. By acknowledging what cannot happen, we can evaluate potential outcomes more effectively.
Risk assessment
Impossible events also play a role in risk assessment. Identifying outcomes that have zero possibility allows us to focus on more probable and relevant events. This enables us to allocate resources, plan strategies, and make informed decisions based on realistic possibilities.
Probability estimation
Understanding impossible events refines our understanding of probabilities. By recognizing outcomes with zero probability, we can better grasp the relative likelihood of other events. This is particularly important in statistical analysis; where accurate probability estimation is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Why the Probability of Impossible Events is zero?
Let us say we have an impossible event E. This means that “E” cannot happen and the probability of E is zero. We can prove this by using a definition of probability. “Probability is the ratio of favorable outcomes to total possible outcomes”. There are no favorable outcomes, so the probability of E occurring is zero.
Solved Examples of impossible Events
Example 1:
Find the probability of rolling a 7 on a standard six-sided die.
Solution:
The sample space consists of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, representing the possible outcomes when rolling the die. The event of rolling a 7 is impossible since there is no face on the die labeled as 7.
Therefore, the probability of rolling a 7 on a standard six-sided die is 0.
Example 2:
What is the probability of selecting a purple marble from a bag with only red and blue marbles?
Solution:
The event selecting a purple marble from this bag is impossible because no purple marbles are available to be chosen.
Thus, the probability of selecting a purple marble is 0.
Example 3:
Determine the probability of flipping a coin and getting both heads and tails simultaneously
Solution:
Flip a fair coin. The possible outcomes are heads (H) or tails (T).
The event of getting both heads and tails at the same time is impossible since the coin can only show one side at a time.
The probability of getting both heads and tails is zero.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the concept of impossible events. We discussed its definition and types. We described the application of impossible events in our daily lives. We have provided the solution of many examples for you.
